Facilities
-
Out Patient Services
Working hours daily 9 am to 9 pm, except Sundays and official holidays, Urgent Consultations on walk-in basis & more
-
In-Patient Services
Full facility for high quality in-patient care, Air Conditioned facilities with a backup in-house generator& more
-
Physiotherapy
Equipped with state of the art modalities like ultra sound, TENS, CPM, muscle stimulators etc. & more
01.ORTHOPAEDIC INFO
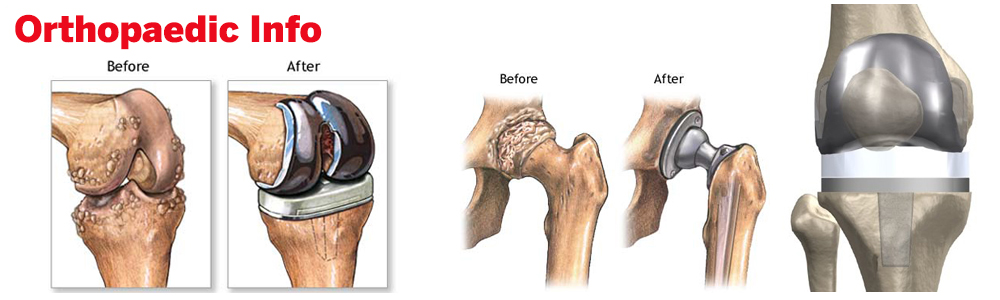
Our institute specializes in Joint Replacement, Hip, Knee, Shoulder, Elbow, Small joints of hand, Arthroscopic Surgery (ACL, PCL, MCL) & more
02.CARE ADVICE
We have a Team of consultants who are very highly qualified and richly experienced. Our consultants give top notch advice to our patients
03.CONTACT US
Institute of Orthopaedics & Surgery always allow their patients to inquire about their questions anytime. You can fill the request through contact form
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a surgical procedure by which the internal structure of a joint is examined for diagnosis and/or treatment using a tube-like viewing instrument called an arthroscope. Arthroscopy was popularized in the 1960s and is now commonplace throughout the world. Typically, it is performed by orthopedic surgeons in an outpatient setting. When performed in the outpatient setting, patients can usually return home after the procedure
The technique of arthroscopy involves inserting the arthroscope, a small tube that contains optical fibers and lenses, through tiny incisions in the skin into the joint to be examined. The arthroscope is connected to a video camera and the interior of the joint is seen on a television monitor. The size of the arthroscope varies with the size of the joint being examined. For example, the knee is examined with an arthroscope that is approximately 5 millimeters in diameter. There are arthroscopes as small as 0.5 millimeters in diameter to examine small joints such as the wrist.
If procedures are performed in addition to examining the joint with the arthroscope, this is called arthroscopic surgery. There are a number of procedures that are done in this fashion. If a procedure can be done arthroscopically instead of by traditional surgical techniques, it usually causes less tissue trauma, results in less pain, and may promote a quicker recovery.
