Facilities
-
Out Patient Services
Working hours daily 9 am to 9 pm, except Sundays and official holidays, Urgent Consultations on walk-in basis & more
-
In-Patient Services
Full facility for high quality in-patient care, Air Conditioned facilities with a backup in-house generator& more
-
Physiotherapy
Equipped with state of the art modalities like ultra sound, TENS, CPM, muscle stimulators etc. & more
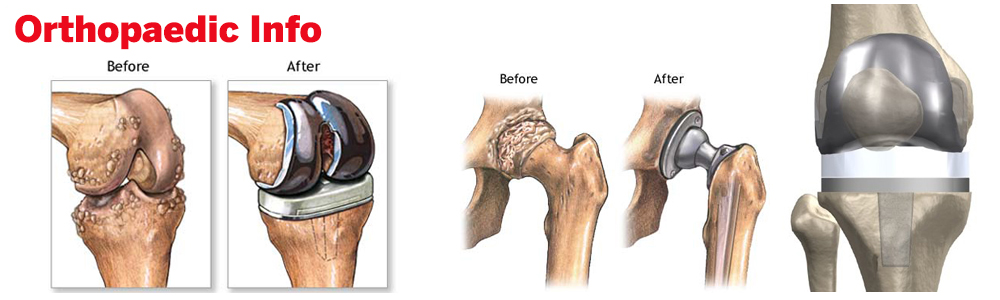
01.ORTHOPAEDIC INFO
Our institute specializes in Joint Replacement, Hip, Knee, Shoulder, Elbow,Small jointsof hand, Arthroscopic Surgery (ACL, PCL, MCL) & more
02.CARE ADVICE
We have a Team of consultants who are very highly qualified and richly experienced. Our consultants give top notch advice to our patients
03.CONTACT US
Institute of Orthopaedics & Surgery always allow their patients to inquire about their questions anytime. You can fill the request through contact form
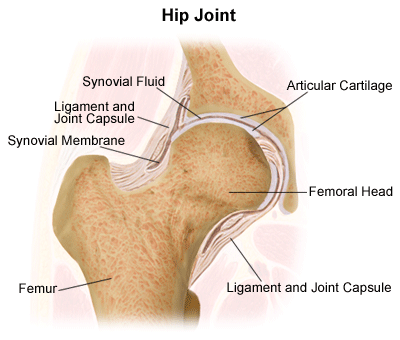
Hip Joint Replacement
|
The surgeon makes an incision along the top of the thigh bone (femur) and pulls the thigh bone away from the socket of the hip bone (the acetabulum). An artificial socket made of metal coated with polyethylene (plastic) to reduce friction is inserted in the hip. The top of the thigh bone is cut, and a piece of artificial thigh made of metal is fitted into the lower thigh bone on one end and the new socket on the other.
|