Facilities
-
Out Patient Services
Working hours daily 9 am to 9 pm, except Sundays and official holidays, Urgent Consultations on walk-in basis & more
-
In-Patient Services
Full facility for high quality in-patient care, Air Conditioned facilities with a backup in-house generator& more
-
Physiotherapy
Equipped with state of the art modalities like ultra sound, TENS, CPM, muscle stimulators etc. & more
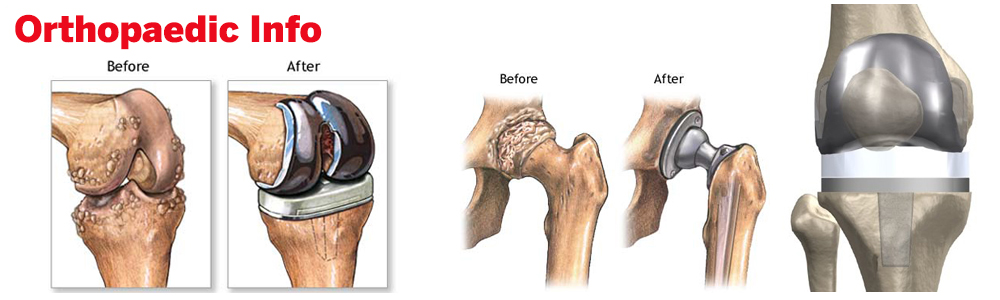
01.ORTHOPAEDIC INFO
Our institute specializes in Joint Replacement, Hip, Knee, Shoulder, Elbow,Small jointsof hand, Arthroscopic Surgery (ACL, PCL, MCL) & more
02.CARE ADVICE
We have a Team of consultants who are very highly qualified and richly experienced. Our consultants give top notch advice to our patients
03.CONTACT US
Institute of Orthopaedics & Surgery always allow their patients to inquire about their questions anytime. You can fill the request through contact form
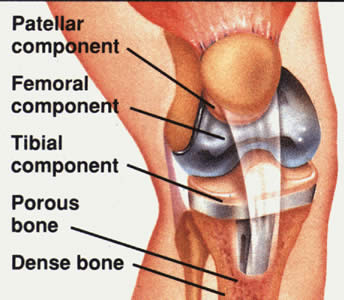
Knee Joint Replacement
|
Both chronic osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis commonly cause people to lose knee function to the degree that they need a knee joint replacement (total knee arthroplasty or TKA). But knee damage may also stem from injury or infection. Generally, people require a TKA a decade earlier due to rheumatoidarthritis as opposed to osteoarthritis
|