Facilities
-
Out Patient Services
Working hours daily 9 am to 9 pm, except Sundays and official holidays, Urgent Consultations on walk-in basis & more
-
In-Patient Services
Full facility for high quality in-patient care, Air Conditioned facilities with a backup in-house generator& more
-
Physiotherapy
Equipped with state of the art modalities like ultra sound, TENS, CPM, muscle stimulators etc. & more
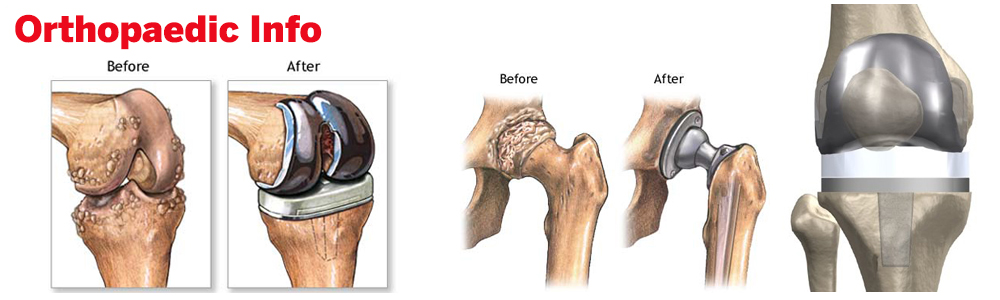
01.ORTHOPAEDIC INFO
Our institute specializes in Joint Replacement, Hip, Knee, Shoulder, Elbow,Small jointsof hand, Arthroscopic Surgery (ACL, PCL, MCL) & more
02.CARE ADVICE
We have a Team of consultants who are very highly qualified and richly experienced. Our consultants give top notch advice to our patients
03.CONTACT US
Institute of Orthopaedics & Surgery always allow their patients to inquire about their questions anytime. You can fill the request through contact form
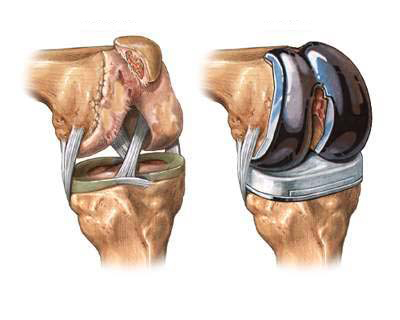
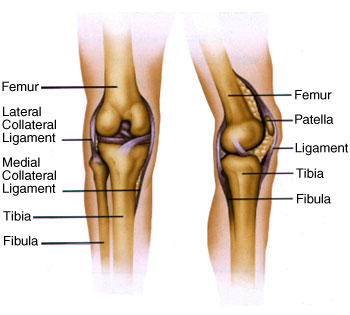
Joint Replacement
|
Joint replacement is the surgical replacement of a joint with an artificial prosthesis. A prosthesis is a device designed to replace a missing part of the body or to make a part of the body work better
|
When to Seek Medical Care Call your family doctor or orthopedist if you develop gradual pain that feels like slippage in your knee. This generally is an urgent problem, but not an emergency. Call your doctor if you notice unexpected drainage from or poor healing of a recent surgery, increasing swelling, or warmth. Go to the hospitalís emergency department if you experience any of the following: A fracture or dislocation after a fall New swelling Redness, or warmth at a joint suggesting infection Swelling, pain, or redness below your knee that suggests a clot in your vein (deep venous thrombosis or DVT)
Procedures
The doctor puts a tourniquet above the knee, than makes a cut to expose the knee joint. The ligaments surrounding the knee are loosened, then the shin bone and thigh bone are cut and the knee removed. The artificial knee is then cemented into place on the remaining stubs of those bones. The excess cement is removed, and the knee is closed. Hospital stays range from three to six days. In both types of surgery, preventing infection is very important. Antibiotics are given intravenously and continued in pill form after the surgery. Fluid and blood loss can be great, and sometimes blood transfusions are needed.
Preparation
Many patients choose to donate their own blood for transfusion during the surgery. This prevents any blood incompatibility problems or the transmission of blood-borne diseases. Prior to surgery, all the standard preoperative blood and urine tests are performed, and the patient meets with the anesthesiologist to discuss any special conditions that affect the administration of anesthesia. Patients receiving general anesthesia should not eat or drink for 10 hours prior to the operation.
Aftercare
Immediately after the operation the patient will be catheterized so that he or she will not have to get out of bed to urinate. The patient will be monitored for infection. Antibiotics are continued and pain medication is prescribed. Physical therapy begins (first passive exercises, then active ones) as soon as possible using a walker, cane, or crutches for additional support. Long term care of the artificial joint involves refraining from heavy activity and heavy lifting, and learning how to sit, walk, how to get out of beds, chairs, and cars so as not to dislocate the joint.
Risks
The immediate risks during and after surgery include the development of blood clots that may come loose and block the arteries, excessive loss of blood, and infection. Blood thinning medication is usually given to reduce the risk of clots forming. Some elderly people experience short term confusion and disorientation from the anesthesia. Although joint replacement surgery is highly successful, there is an increased risk of nerve injury. Dislocation or fracture of the hip joint is also a possibility. Infection caused by the operation can occur as long as a year later and can be difficult to treat. Some doctors add antibiotics directly to the cement used to fix the replacement joint in place. Loosening of the joint is the most common cause of failure in hip joints that are not infected. This may require another joint replacement surgery in about 12% of patients within a 15-year period following the first procedure.
Normal results
Over 90% of patients receiving hip replacements achieve complete relief from pain and significant improvement in joint function. The success rate is slightly lower in knee replacements, and drops still more for other joint replacement operations
| Knee Joint Replacement | Hip Joint Replacement |